How to wind up a company?
How to wind up a company? It is a very important question which a professional must know the answer of.
I am sharing here some useful guide for the procedure and legal requirements to wind up a company. I hope that it will be equally useful for the professionals and students of Chartered Accountancy.
The term ‘winding up’ of a company may be defined as the proceedings by which a company is dissolved (i.e. the life of a company is put to an end). Thus, the winding up is the process of putting an end to the life of the company. And during this process, the assets of the company are disposed of, the debts of the company are paid off out of the realized assets or from the contributories and if any surplus is left, it is distributed among the members in proportion to their shareholding in the company. The winding up of the company is also called the ‘liquidation’ of the company. The process of winding up begins after the Court passes the order for winding up or a resolution is passed for voluntary winding up. The company is dissolved after completion of the winding up proceedings. On the dissolution, the company ceases to exist. So, the legal procedure by which the existence of an incorporated company is brought to an end is known as winding up.
 Modes of winding up
Modes of winding up
The winding up of a company may be either-
(i) by the Court; or
(ii) voluntary; or
(iii) subject to the supervision of the Court
- PROCEDURE FOR WINDING UP OF COMPANY AND FILING OF PETITION BEFORE RESPECTIVE HIGH COURT:
-
- To pass Special Resolution by 3/4th majority of the members of the company
that the company be wound up by the Court in case if the company itself intend
to file a petition and to file the Special Resolution on Form 26 with the
registrar. - To prepare a list of the assets to ascertain that the company is unable to pay its
debts. - To prepare a list of the creditors
- In case of defaults in payments the creditor or creditors to make a decision for
the filing of the winding up petition. - In case if the Commission or Registrar or a person authorised by the
Commission intend to file a petition, they should not file a petition, for winding
up of the company, unless an investigation into the affairs of the company has
revealed that it was formed for any fraudulent or unlawful purpose or that it is
carrying on a business not authorised by its memorandum or that its business
 is
is
being conducted in a manner oppressive to any of its management has been
guilty of fraud, misfeasance or other misconduct towards the company or
towards any of its members. - To engage advocates for the preparation and filing of the petition.
- To pass Special Resolution by 3/4th majority of the members of the company
- PROCEDURE FOR VOLUNTARY WINDING UP
The following steps are to be taken for Member’s voluntary winding up under the Provisions of the Ordinance, and the Companies Rules.
Step 1. Where it is proposed to wind up a company voluntarily, its directors make a declaration of solvency on Form 107 prescribed under Rule 269 of the Rules duly supported by an auditors report and make a decision in their meeting that the proposal to this effect may be submitted to the shareholders. They, then, call a general meeting (Annual or Extra Ordinary) of the members (Section 362 of the Ordinance)
Step 2. The company, on the recommendations of directors, decides that the company be wound up voluntarily and passes a Special Resolution, in general meeting (Annual or Extra Ordinary) appoints a liquidator and fixes his remuneration. On the appointment of liquidator, the Board of directors ceases to exist. (Sections 358 and 364 of the Ordinance)
Step 3. Notice of resolution shall be notified in official Gazette within 10 days and also published in the newspapers simultaneously. A copy of it is to be filed with registrar also. (Section 361 of the Ordinance)
Step 4. Notice of appointment or change of liquidator is to be given to registrar by the company alongwith his consent within 10 days of the event. (Section 366 of the Ordinance)
Step 5. Every liquidator shall, within fourteen days of his appointment, publish in the official Gazette, and deliver to the registrar for registration, a notice of his appointment under section 389 of the Ordinance on Form 110 prescribed under Rule 271 of the Rules.
Step 6. If liquidator feels that full claims of the creditors cannot be met, he must call a meeting of creditors and place before them a statement of assets and liabilities. (Section 368 of the Ordinance)
Step 7. A return of convening the creditors meeting together with the notice of meeting etc. shall be filed by the liquidator with the registrar, within 10 days of the date of meeting. (Section 368 of the Ordinance)
Step 8. If the winding up continues beyond one year, the liquidator should summon a general meeting at the end of each year and make an application to the Court seeking extension of time. (Section 387(5) of the Ordinance)
Step 9. A return of convening of each general meeting together with a copy of the notice, accounts statement and minutes of meeting should be filed with the registrar within 10 days of the date of meeting. (Section 369 of the Ordinance)
Step 10. As soon as affairs of the company are fully wound up, the liquidator shall make a report and account of winding up, call a final meeting of members, notice of convening of final meeting on Form 111 prescribed under Rule 279 of the Rules before which the report / accounts shall be placed. (Section 370 of the Ordinance)
Step 11. A notice of such meeting shall be published in the Gazette and newspapers at least10 days before the date of meeting. (Section 370 of the Ordinance).
Step 12. Within a week after the meeting, the liquidator shall send to the registrar a copy of the report and accounts on Form 112 prescribed under Rule 279 of the Rules. (Section 370 of the Ordinance)
- PROCEDURE FOR CREDITOR’S VOLUNTARY WINDING UP
Step 1. First of all, the company passes a special resolution in the general
meeting of the members of the company for which following steps are to taken:
- Board of Directors approves the agenda of the general meeting especially the draft special resolution for winding up of the company.
·Notice of the general meeting alongwith copy of the draft special resolution is given to the members at least 21 days before the general meeting.
·Special resolution is passed by 3/4th majority of the members of the company and the members appoint a person to be liquidator of the company.
·Special resolution on Form 26 is filed with the registrar.
Step 2 . Meeting of creditors is called at 21 days notice, (simultaneously with sending of the notices of the general meeting of the company) the notice of the meeting of the creditors to be send by post to the creditors, besides, the notice of the said meeting to be advertised in the official Gazette and the newspaper circulated in the Province and the creditors pass a resolution of voluntary winding up of the company. The creditors also appoint liquidator in that meeting. If the creditors and the company nomina te different persons, than person nominated by the creditors shall be liquidator.
Step 3. Notice of the resolution passed at the creditor’s meeting shall be
given by the company to the registrar alongwith consent of the liquidator within ten
days of the passing of the resolution.
The company may either at the meeting at which resolution for voluntary winding
up is passed or at any subsequent meeting may, if they think fit, appoint a committee of inspection consisting of not more than five persons. Provided that the creditors may, if they think fit, resolve that all or any of the person so appointed by the company ought not to be member of the committee of inspection.
Step 4. The liquidator should, with all convenient speed, realise the assets, prepare lists of creditors, admit proof, settle list of contributories, make such calls as may be necessary, etc. accordingly as the nature of the case may require, pay secured creditors, pay the costs including the liquidator’s own remuneration, pay preferential claims, and after meeting all the claims of creditors, and after adjusting all claims and rights, distribute the surplus on pro rata basis.
Step 5. In the event of the winding up continuing for more than one year, the liquidator shall summon a general meeting of the company and a meeting of creditors at the end of the first year from the commencement of the winding up and lay before the meetings an audited account of receipts and payments and acts and dealings and of the conduct of winding up during the preceding year together with a statement in the prescribed form and containing the prescribed particulars with respect to the proceedings and position of liquidation and forward by post to every creditor and contributory a copy of the account and statement together with the auditors’ report and notice of the meeting at least ten days before the meeting required to be held.
Step 6. The liquidator prepares the accounts, gets them audited and also presents a final report to the creditors. The steps at this stage are as under:
·The liquidator prepares a final report and accounts of the winding up, showing how the winding up has been conducted and the property of the company have been disposed of.
·Accounts are duly audited by the auditor appointed for the purpose.
·The notice of meeting is sent by post to each contributory of the company and creditor at least ten days before the meeting. The account with a copy of the auditor’s report is also enclosed with the notice.
·The notice of the meeting specifying the time, place and object of the meeting is published at least ten days before the date of the meeting in the official Gazette and in at least one newspaper.
·Within one week after the meeting, the liquidator is required to send to the registrar a copy of his report and account, and make a return to him of the holding of the meeting alongwith the minutes of the meeting.
·If a quorum is not present at the meeting, the liquidator makes a return stating that the meeting was duly summoned and that no quorum was present thereat. The return is filed with the registrar and considered as presented in the meeting.
·The registrar, on receiving the report, account and the return, is required to register them after their scrutiny.
·On the expiration of three months from the registration of final report, accounts and minutes, the company is deemed to be dissolved
- For more details please see
SECP guide on winding up
MS Office product key
9PXQN-JVDCB-7F4VW-6KVJ2-2DJ8W THD8P-7N47Y-73Y8K-T4YK3-2WFPJ FWVGN-7J3C2-QWW79-FY9KT-Y98CJ YJMG6-DT2V7-3J6D3-KVF2M-PR3R8 3P24Q-RVNMM-VYTK4-8R2W7-BDWCJ KP2N2-4GB7B-XCXY9-QREDJ-33WCJ 2QD4N-RG86W-Y9KR3-C98XK-D9K48 NH7D3-QXMPD-46DM6-M4GX3-G82WW RQ9NM-Q6GRX-4QQ29-D77LY-3GM2J RNWDP-TVWFW-7CYKX-877F4-F6X48 R6TN2-W9PF6-79YD9-VT734-843R8 QPR86-NF2M2-23HJN-TFRHX-DYHF8 QKYQV-36NGX-Y7X88-V3M3B-G2948 Q6NWY-D3BR4-YRHDH-2VKT7-94RPJ PJNQH-HXPGK-VWR96-8896M-PYTJW YNKQH-9KQ4V-HTV6H-DB8W5-K2DR8 YNDM3-JGYFK-WX7F6-KWHK6-QYHF8 YYCQ3-6GB4D-6696Y-3BP63-GF4QP NXG3H-RMGEX-8YDWT-3K6WK-GJGK2 PKQR9-PXNG2-4GGK2-C3K7M-JK8CJ 4JXPB-N9HK4-GQ3G8-GV6HD-KKX7C 42RKN-YXH86-282MH-EG747-3J3VC WF4NK-RVKYM-MG7QJ-BYT9E-2PQVC JND3F-KHYQQ-QMYY4-BW3WP-FX892 QV6W9-3XNKH-8JRCK-RYKKM-DPDR8 NBPPC-GJTD4-B3KQX-F7G9P-PGX48 QNP2R-B9X63-JRH2P-87Y7H-XD7F8 2JDF3-MTNJ9-KVB99-BWODT-9KW8W WRX7N-M98K9-B82K8-KEQ4W-D9K48 MNX3P-M9C2M-XD23P-F2KKT-KTM2J RKJTF-HNYXC-DC9D8-8RQ3G-BPY2J HFYWB-YQN3V-Y9XEV-3TRCC-J43R8TN786-9K9FW-8VR7C-7MH7G-V6DVC GFNRH-4TH9M-XYCQ4-7NGJJ-PKB2J FYG4P-ND86E-JR9RG-8DVDX-HCDR8 FD324-NYKDT-JGC3K-DCHTH-BDWCJ F689N-699KK-P2JMJ-C9QH7-2R3R8 C2CRN-Q8HGX-Q7QKP-974KG-RRGJW
How to differentiate Bill of Lading and Master Bill of Lading?
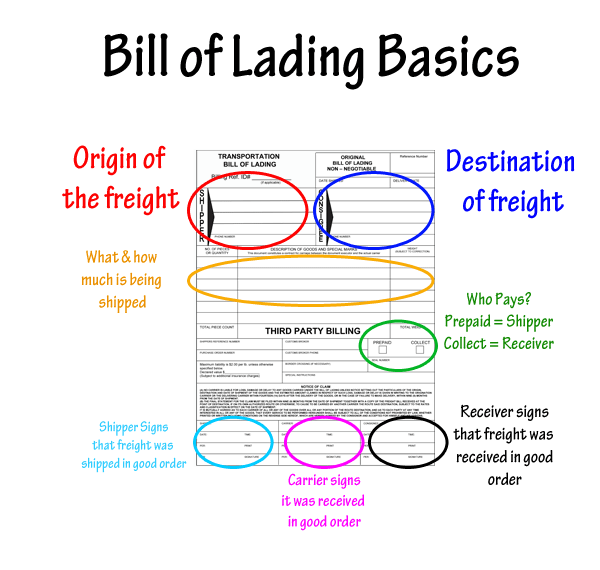 What is Bill of lading? How Master Bill of Lading differentiate from Bill of Lading.
What is Bill of lading? How Master Bill of Lading differentiate from Bill of Lading.
If you know about bill of lading and master bill of lading, you can differentiate both. Let us discuss what is Bill of lading and how does bill of lading work.
Bill of lading is a document issued by sea carrier of goods on receipt of cargo to him from the shipper (a person or company that transports or receives goods by sea, land, or air.). Bill of lading is issued to shipper after completion of export customs clearance procedures at load port customs location of the country.
After completion of export customs formalities, shipper hands over cargo to sea shipping carrier or his agent. As proof of receipt of goods, sea carrier or his agent issues a document which is called bill of lading (BL). Bill of lading is generally issued in triplicate with non negotiable copies. BL also is issued in quintuplicate (fivefold, multiply by five) on special request by shipper.
Once after obtaining original bill of lading from the sea carrier, shipper submits bill of lading with other documents with his bank, in turn bank sends to importer through importer’s bank. Importer collects bill of lading and other required documents from his bank and arranges for import customs clearance procedures. The shipper can surrender original bill of lading at load port where BL has been released and arranges to send a OBL release message to the counterpart office of sea carrier and advise them to release cargo without insisting for original bill of lading from consignee. The shipper also can release Seaway bill where in no original bill of lading procedures involved.
What is MBL master bill of lading and how does it work?
MBL means Master Bill of Lading issued by vessel owner or his agent to a freight forwarder on receipt of goods from shipper agreeing to deliver goods at destination.
Practical scenario:
A, a freight forwarder acts as a carrier legally accepts cargo from an exporter X agreeing to deliver cargo to Y at New York. A issues bill of lading to X on receipt of goods after necessary export customs formalities. A after receiving goods from X transfers goods to C who is a main carrier of goods. While transferring goods to C, A obtains a bill of lading from main carrier C agreeing to deliver cargo at New York. Here, the bill of lading issued by A to X is called house bill of lading and the bill of lading issued by C to A is called Master Bill of Lading.
Conclusion:
Have you cleared your doubt yourselves about the difference between Bill of Lading and Master Bill of Lading?. Ok, let me conclude below the major differences between BL and MBL:
Bill of lading (BL) is a document, which is a proof of receipt of goods from shipper issued by sea carrier after completing export customs clearance procedures and formalities. If a freight forwarder delivers goods received from final shipper to main sea shipping carriers and obtains document of receipt of goods which is called Master Bill of Lading (MBL). In turn, said freight forwarder issues bill of lading to final shipper which is called House Bill of Lading (HBL).
Remember:
All Master Bills of Lading (HBL) are Bills of Lading, but all Bills of Lading need not be Master Bills of Lading. Correct? ∞
THE BIG 4 Interview Questions

The interview questions of PWC
PWC really, really, really likes competency interview questions. The company lists the competencies it works for here. It also provides a few transcripts of past interview questions and answers here.
And these are all the questions that candidates (and PWC itself) says it likes to ask:
1. Tell me about a time you had to correct someone’s mistake
2. What do you think this role involves?
3. Describe a time when you had to improve a piece of work after criticism?
4. What have you read about PWC in the news?
5. Can you describe a time when you have worked in a team to deliver a piece of work? – What was your role in the team? What did you do exactly?
6. Describe a time when you’ve successfully managed a project for example coursework or organising an event. What challenges did you overcome? Who supported you? What was the outcome?
7. Can you tell me about a piece of recent financial news you’ve read? Why did you find it interesting?
8. Give an example of a time you failed to accomplish something.
9. Give an example of a time you built a relationship.
10. Why audit?
11. Give an example of a time you worked with someone with a different style. How did this differ to your own?
12. Give an example of a time you said something unethical.
13. Give an example of a time when you weren’t given enough guidance.
14. Why PWC?
15. Give an example of a time you overcame conflict.
16. What do you know about the ACA exams?
17. Give an example of a time when you worked with people outside your usual network.
18. What’s the most difficult thing about working with you?
19. Give an example of a time you solved a complex problem.
20. Give an example of a time when you had to complete multiple different projects to a short deadline.
The interview questions of Deloitte
Much like PWC, Deloitte loves competency interviews. You can see the firm’s seven key
competencies listed here. Be prepared to answer very detailed questions about times you’ve demonstrated these competencies in the past.
Below are the questions that previous candidates and Deloitte itself say you should expect in an interview with the firm. Brainteasers appear to crop up from time to time.
1. Describe your role in a piece of work you’re particularly proud of.
2. Describe a time you collaborated with others to achieve a goal.
3. Give me an example of when you have dealt with a difficult character
4. How would people describe you in three words?
5. Why Deloitte?
6. Why audit?
7. Talk me through a long term project you’ve been involved in.
8. Why did you study a university degree if you want to work in accountancy?
9. What’s good about you?
10. Describe a time you defended a friend.
11. How would you sell yourself?
12. Which other companies are you applying to?
13. Describe a time when you had to settle upon the right course of action. What were your thought processes when you made this decision?
14. How do you try to be the best you can be?
15. Tell us about a time you led a team.
16. What can you bring to Deloitte?
17. How do you handle stress at work?
18. Tell me about a time you adapted to an unfamiliar situation.
19. Why are pot holes round?
20. How many pens can I fit in this room?
The interview questions of KPMG
What will you be asked in an interview at KPMG? The short answer is more of the same again.
KPMG lists its nine behavioural competencies here. When you interview with the firm, you’ll be asked a lot of questions about when you demonstrated them.
For example….
1. What makes KPMG different from the rest of the Big Four? Why do you want to work here?
2. What’s the difference between an internal auditor and an external auditor?
3. What do you think this job will involve exactly?
4. Talk about a time you’ve managed multiple tasks to finish a project for a deadline.
5. Talk about a time you worked in a team where there were communication problems. How did you help resolve them?
6. Can you talk about a time you’ve had to deal with a difficult customer? How did you diffuse the situation?
7. What’s good about you? What’s not? What do you need to learn?
8. Can you give an example of a time when you’ve had to communicate an idea persuasively in writing?
9. Can you tell me something interesting you’ve read about KPMG in the news?
10. Can you tell me about a time when circumstances changed? How did you adapt?
11. Can you tell me about a time when you’ve had to overcome a setback? How did you overcome it?
12. Can you talk about a business that’s doing well? Which three things do you consider key to their success?
13. Can you talk about a business that’s doing badly? Which problems does it face?
14. Can you talk about a time when you’ve motivated a team to work together? What did you d exactly?
15. What are you most proud of?
16. Which opportunities can you see now for KPMG to develop new business?
17. Which skills do you think you’ll need in the role you’re applying for at KPMG?
18. Can you tell me about a time you felt bored at work? How did you make the job more interesting?
19. Can you talk us through the way you evaluated a challenging situation in the past?
20. A company wants to relocate overseas. Talk us through the problems it faces.
The interview questions of EY
Finally, EY has those ‘strengths’ interviews. Strengths interviews are all about finding out your interests and what you’re good at. The interviewer wants to know what you’re really like. In recruiter parlance, they want to know your ‘authentic self.’
To this end, candidates and the firm itself say you should expect the following questions when you interview at EY.
1. What are you good at?
2. What do you most enjoy studying?
3. What gives you a buzz?
4. Are you a starter or a finisher?
5. Are you into big picture or detail?
6. Describe a successful day you had recently.
7. What do you love doing in your spare time?
8. When are you happiest?
9. When you do you feel most like yourself?
10. Do you find there are enough hours in the day?
11. Have you ever done something differently the second time around?
12. Tell me about your friends.
13. Which three words would you friends use to describe you?
14. What’s your biggest weakness?
15. Have you ever wanted to stop doing something?
16. Do you think you need to be an expert to lead a team?
17. Would you say you’re organized? Would your friends?
18. Do you enjoy hard work?
19. Why do you want this job?
20. Give an example of a time you asked for more responsibility.
Difference between DA and DP/DAP terms of payment
DA in payment term of international trade means, Documents against Acceptance.
DP in payment term of imports and exports means Documents against Payments.
How to distinguish between Documents against Acceptance and Documents against Payment in Exports and Impor ts?
ts?
Both DA and DP are the terms of payment related to acceptance of shipping documents pertaining to each consignment from buyer’s bank. Under a DA terms of payment, importer accepts documents on the basis of an assurance to effect payment by accepting necessary bill of exchange. The importer collects shipping documents required to take delivery of imported goods from his bank after such assurance on payment at mutually agreed maturity date of payment.
In a DP payment terms, the imported need to effect payment against respective import consignment, before collecting documents for delivery of imported goods. Under a payment terms – Documents against Payments, the bank delivers documents required for import clearance only after receiving the value of goods from the importer. The buyer takes delivery of goods with the original transport document of title delivered by his bank after effecting payment under sale of goods mentioned in the document. The buyer’s bank in turn, sends the said amount to seller’s bank as per banking procedures and formalities under international trade.
IFRS at glance 2016
Dear fellows today I am going to share with you a most valuable document. This will be very useful for you in your entire financial reporting career. Either you are a student of accountancy or practicing Chartered Accountant, this document will help you.
IFRS at glance is very necessary for all those in the field of accountancy. This document contains all the updates in the Standards, Interpretations and Amendments upto 2016.
For a student it is very difficult to make the concise notes on International Financial Reporting Standards IFRS which will be helpful at the time of revision before exam. This document will be helpful for such students. click here.
It will also help those professionals either in practice or in industry who want a ready reference to IFRS. For me I found it very helpful both in my studies and also in my practice that is the reason I wanted to share it with my dear fellows. Hope it will help you too.
PROFESSIONAL EMAIL SENTENCES
Sentences to make your email look professional: “Further to your mail of today, I have a great pleasure to confirm your reservation for the date mentioned below:” “Looking forward to welcome you to__________ hotel, Dubai and assuring you of our best services at all times”. “It is with great pleasure to confirm ……..” “Thank you for your recent enquiry regarding…..” “Below you will find a summary of your request…..” “Your co-operation on the above would be highly appreciated”. “Once again thank you, awaiting to welcome your guest at _________hotel”. “In response to your mail dated…….we are glad to inform you that we have reserved as follows:” “Hope you find this helpful”. “Hope this is clear enough; feel free to start right away. Thank you”. “Thank you for your time & prompt attention”. “Your prompt reply will be solicited”. “Will revert back to you shortly”. “Many thanks again for your time”. “I trust the above resolves your queries. Should you have any further questions, please don’t hesitate to contact me”. “Hope the above helps, email again if you still having any difficulties”. “Thanks! I appreciate your help”. “With regards to our conversation over the phone” Please ignore my previous mail; sorry for the confusion consider the attached as latest” “I would appreciate your immediate attention to this matter” “We regret the in-convenience caused & thank you for your usual co-operation”. “Kindly acknowledge the same” “Appreciate if you could take this on your urgent consideration to check.” . To take some action: “I would appreciate your help in this matter”. “Would you mind checking it out for me? Thanks in advance”. “Can you get back to me once you have time for it?” “I’d love to hear your advice on this”. . Need a response: “I await a response at your earliest convenience”. “Look forward to hearing from you”. “Can you drop me a quick word, so I know you’ve received this?” . Heard nothing & want to chase: “In reference to my mail of________ (month)” “When you get a moment could you drop me a line about my last mail?” “Any updates so far?” “Could you please advice for the below request sent” “Drop me an email when you will have an update on previous mail”. “I am yet to receive an update from your end, requesting you to revert ASAP”.







